自然共生を実現するための持続的な川づくりと流域管理の戦略
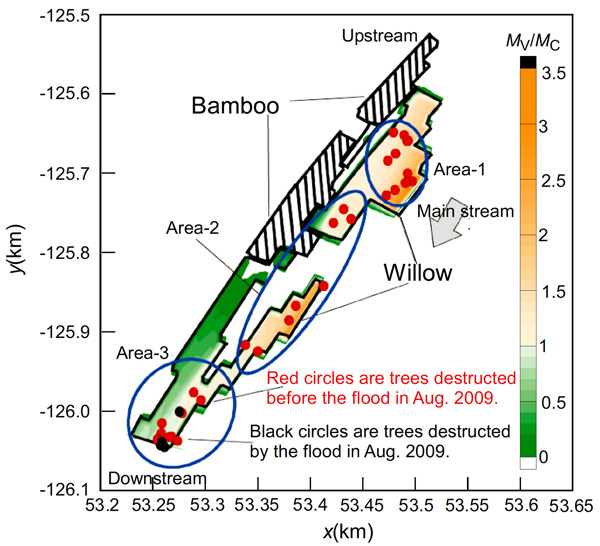
適切な計画の下で河川の整備や管理を実施しないと、河川本来の流れや地形に不可逆的な変化を与え、水辺の景観や水質・生態系など自然環境を損ねることがあります。当研究室では、安全で自然との共生を実現するための持続的な川づくり、環境負荷を緩和・最小化するための流域管理の戦略について研究します。
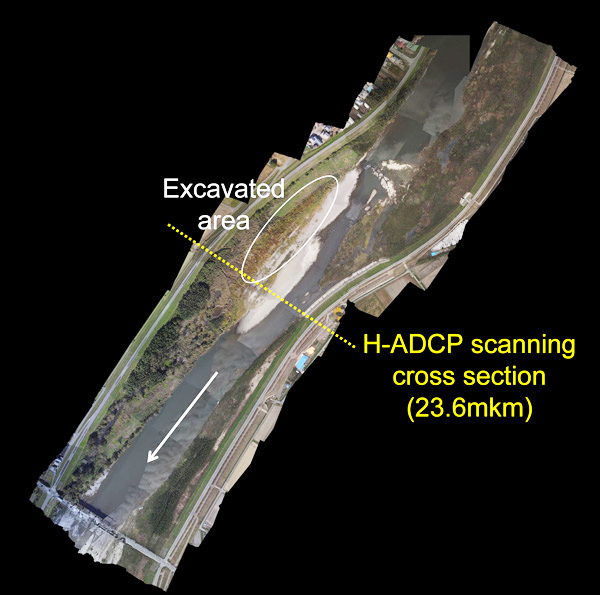
様々なインフラの劣化と維持管理は、これからの最も重要な技術課題として注目されています。自然公物である河川は、人為的な管理・利用と気候変動の影響を受けて環境水理学的な特性が変動するため、経年的に劣化する人工構造物とは異なる管理概念が必要となります。水辺から流域に至るまでの様々な規模の空間を対象に川のデザイン戦略を考えていきます。
Environmental hydraulics, sustainability in hydrosphere, water quality management in lakes and reservoirs
A sustainable management and wise use of water is the most critical and challenging issue in the next era. Various environmental problems in river channels and catchments are investigated focusing on hydrodynamics, water quality and ecology that are playing important roles in human's activities and nature. Hydraulic analysis of fluvial channels, sustainable management of vegetated rivers, water quality management in lakes and reservoirs, micro-bubble aeration of anoxic water are examples of our research interests. Not only field works but also computational analysis is carried out in order to find out hydrodynamic and ecological processes in the hydrosphere in river catchments. Our goal is to provide an engineering design tool for creating a river catchment that has a symbiotic relationship with local and global societies.